- Prediction of Post-resection Prognosis Using the ADV Score for Huge Hepatocellular Carcinomas ≥13 cm
-
Shin Hwang, Ki-Hun Kim, Deok-Bog Moon, Chul-Soo Ahn, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park
-
J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):45-57. Published online March 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.45
-
-
4,205
Views
-
75
Downloads
-
1
Citation
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background/Aim
s: Multiplication of α-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin, and tumor volume (ADV score) is a surrogate marker for post-resection prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to validate the predictive power of the ADV score-based prognostic prediction model for patients with solitary huge HCC.
Methods
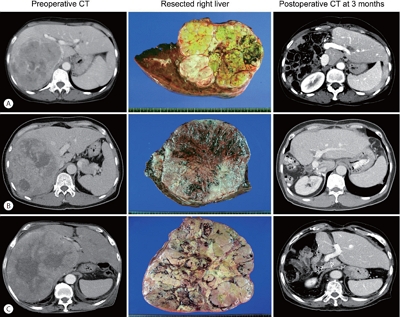
Of 3,018 patients, 100 patients who underwent hepatic resection for solitary HCC ≥13 cm between 2008 and 2012 were selected.
Results
The median tumor diameter and tumor volume were 15.0 cm and 886 mL, respectively. Tumor recurrence and overall survival (OS) rates were 70.7% and 66.0% at one year and 84.9% and 34.0% at five years, respectively. Microvascular invasion (MVI) was the only independent risk factor for disease-free survival (DFS) and OS. DFS and OS, stratified by ADV score with 1-log intervals, showed significant prognostic contrasts (P=0.007 and P=0.017, respectively). DFS and OS, stratified by ADV score with a cut-off of 8-log, showed significant prognostic contrasts (P=0.014 and P=0.042, respectively). The combination of MVI and ADV score with a cut-off of 8-log also showed significant prognostic contrasts in DFS (P<0.001) and OS (P=0.001) considering the number of risk factors. Prognostic contrast was enhanced after combining the MVI and ADV score.
Conclusions
The prognostic prediction model with the ADV score could reliably predict the risk of tumor recurrence and long-term patient survival outcomes in patients with solitary huge HCCs ≥13 cm. The results of this study suggest that our prognostic prediction models can be used to guide surgical treatment and post-resection follow-up for patients with huge HCCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - ADV score is a reliable surrogate biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma in liver resection and transplantation
Shin Hwang, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gi-Won Song
Annals of Liver Transplantation.2023; 3(2): 86. CrossRef
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Pregnant Patient in Twenties
-
Kang Kook Choi, Young Ju Hong, Sae Byeol Choi, Nam Joon Yi, Shin Hwang, Young Nyun Park, Jin Sub Choi, Kyung Suk Suh, Chae Yoon Chon, Kyung Sik Kim
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):76-81. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in pregnancy is very rare. The cirrhosis which is present in the majority of patients with
HCC induces infertility. The diagnostic methods and treatment modalities in HCC during pregnancy are different from those
of usual types of other HCC. A 26-year-old, 32th-gestational-week pregnant female was sent to our hospital because of
abnormal liver function test. A 1.5cm sized mass was identified in segment 6 of liver which was compatible to AJCC stage
I. She did not have any other medical history except Hepatitis B Virus carrier and the HBs Ag of her mother also was
positive. At the 40th gestational week, the female baby was delivered uneventfully. And then she underwent the transarterial
chemoembolization (TACE) following the Rt. Hemihepatectomy. Since she underwent a surgical resection, the tumors have
been recurred in the remnant liver only. Whenever the tumors were founded, the aggressive surgical approaches were
performed including 3 times of hepatic resection with TACE or TACI. She is still alive with good general condition and
normal liver function for 9 years since the first diagnosis was made. Therefore an extremely rare case of hepatocellular
carcinoma in pregnancy is treated successfully because of aggressive therapies.
|